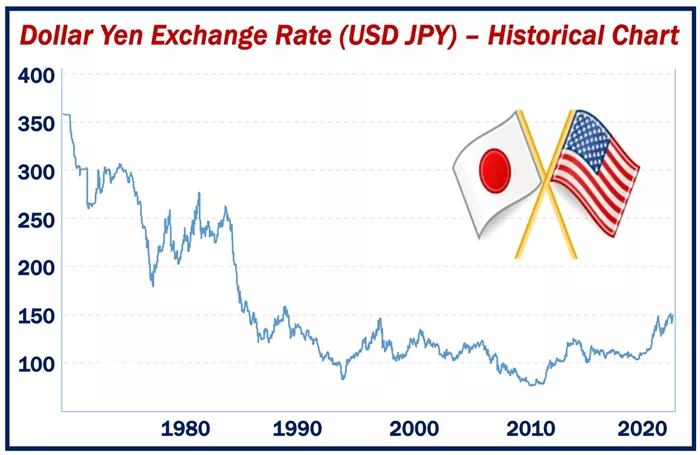
In the ever – churning maelstrom of global foreign exchange, where trillions of dollars’ worth of currencies change hands daily, the conversion of US dollars (USD) into Japanese yen (JPY) stands as a linchpin transaction. This seemingly straightforward exchange wields far – reaching implications, intricately woven into the fabric of international finance and commerce. For international investors, the USD – JPY exchange rate serves as a crucial barometer. It shapes their investment portfolios, dictating whether to pour capital into Japanese equities, bonds, or real – estate. A favorable exchange rate can significantly boost returns, while an adverse movement might erode profits. The ability to accurately navigate this currency conversion can mean the difference between a lucrative investment strategy and a costly misstep.
The Currencies: An Overview
The US Dollar
The US dollar, symbolized as $ and with the currency code USD, is the world’s primary reserve currency. Its dominance in the global financial system stems from the economic might of the United States, the largest economy in the world. The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, plays a pivotal role in shaping the value of the dollar. Through monetary policy tools such as setting interest rates and conducting open market operations, the Fed influences the supply of dollars in the market. For instance, when the Fed raises interest rates, it attracts foreign capital seeking higher returns, increasing the demand for dollars and strengthening its value.
The Japanese Yen
The Japanese yen, denoted by ¥ and with the currency code JPY, is the official currency of Japan. Japan, known for its highly developed and export – oriented economy, has a currency that is widely used in international trade and finance. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) is responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy for the yen. The BOJ’s policies often focus on maintaining price stability and promoting economic growth. Measures such as quantitative easing, where the central bank purchases financial assets to increase the money supply, can have a significant impact on the yen’s exchange rate. A more expansive monetary policy may lead to a depreciation of the yen as the increased supply of currency in the market reduces its relative value.
Exchange Rate Fundamentals
Determinants of the USD – JPY Exchange Rate
The exchange rate between the US dollar and the Japanese yen is determined by a multitude of factors. One of the most influential factors is the interest rate differential between the United States and Japan. When the interest rates in the US are higher than those in Japan, investors are more likely to hold dollars to earn higher returns on their investments. This increased demand for dollars causes the USD to appreciate relative to the JPY.
Economic growth is another crucial factor. A strong economic performance in the United States, characterized by robust GDP growth, low unemployment, and increasing consumer spending, generally leads to a stronger dollar. On the other hand, a thriving Japanese economy, with rising exports and business investments, can strengthen the yen.
Inflation rates also play a role. If inflation in the US is higher than in Japan, the purchasing power of the dollar decreases. In such a scenario, the demand for the yen may increase as it becomes a relatively more stable store of value, leading to a depreciation of the dollar against the yen.
Exchange Rate Quotations
The USD – JPY exchange rate is typically quoted in two ways: direct and indirect. A direct quote shows how many yen are needed to buy one US dollar (JPY/USD). For example, if the exchange rate is 135 JPY/USD, it means that 135 yen are required to purchase 1 US dollar. An indirect quote, conversely, indicates how many US dollars are needed to buy one Japanese yen (USD/JPY). In the above example, the indirect quote would be approximately 0.0074 USD/JPY (1/135). Exchange rates are constantly in flux, reacting to real – time market developments, economic data releases, and geopolitical events.
Methods of Exchanging US Dollars for Japanese Yen
Banks
Banks are a traditional and reliable option for currency exchange. In the United States, major banks like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo offer foreign currency exchange services. To exchange US dollars for Japanese yen at a bank, customers usually need to visit a branch in person. Some banks also provide the convenience of ordering foreign currency online for in – branch pickup or home delivery. However, banks generally impose fees and spreads on currency exchanges. The spread is the difference between the bank’s buying and selling rates for the currency. A wider spread means that customers will receive fewer yen for their dollars, effectively increasing the cost of the exchange.
Currency Exchange Bureaus
Currency exchange bureaus, often located in airports, tourist areas, and major transportation hubs, specialize in foreign currency exchange. In the US, there are numerous independent currency exchange businesses as well as those affiliated with larger financial institutions. These bureaus may offer more competitive rates than some banks, especially for smaller transactions. However, it is essential to be cautious as some bureaus may have hidden fees or less favorable terms. In Japan, similar currency exchange bureaus can be found in popular tourist destinations, where travelers can exchange their dollars for yen upon arrival.
Online Currency Exchange Platforms
The digital age has brought about the emergence of online currency exchange platforms, which provide a convenient and often cost – effective alternative. Platforms such as TransferWise (now Wise), Xe, and OFX allow users to exchange US dollars for Japanese yen with ease. These platforms typically offer competitive exchange rates due to their lower operating costs compared to traditional brick – and – mortar institutions. To use an online platform, users need to create an account, verify their identity, and transfer the US dollars they wish to exchange. The platform then converts the dollars into yen and transfers the funds to the user’s designated Japanese bank account or offers other options for receiving the yen, such as cash pickup at partner locations.
Pre – exchange Considerations
Transaction Costs
Transaction costs associated with exchanging US dollars for Japanese yen can vary significantly depending on the chosen method. As mentioned, banks may charge a combination of a flat fee and a spread. Currency exchange bureaus may have different fee structures, and some may even add additional charges for services like currency delivery. Online platforms usually have transparent fee schedules, often charging a percentage of the total amount being exchanged. It is important for individuals to carefully compare the costs across different providers to ensure they get the best value for their money.
Market Volatility
The foreign exchange market is highly volatile, and the USD – JPY exchange rate can experience rapid fluctuations. News about economic indicators, central bank announcements, and geopolitical events can all cause significant movements in the exchange rate. For those planning to exchange a large amount of US dollars for Japanese yen, it may be beneficial to monitor the exchange rate trends over a period of time. Some may choose to time their exchanges when the rate is more favorable, although accurately predicting market movements is extremely challenging.
Regulatory Requirements
Both the United States and Japan have regulatory frameworks governing currency exchange. In the US, financial institutions are required to comply with anti – money laundering and counter – financing of terrorism regulations. When exchanging dollars for yen, customers may be asked to provide identification documents, such as a passport or driver’s license. In Japan, similar regulations are in place, and there may be restrictions on the amount of currency that can be brought into or out of the country, as well as reporting requirements for large – value transactions.
Conclusion
Exchanging US dollars for Japanese yen is a multifaceted process that involves understanding the characteristics of both currencies, the determinants of the exchange rate, and the various available exchange methods. By being aware of the transaction costs, market volatility, and regulatory requirements, individuals and businesses can make more informed decisions when conducting this currency exchange. Whether for investment, trade, or travel purposes, a comprehensive understanding of the process is essential for navigating the global foreign exchange market successfully.
Related topics:
- Current MXN Exchange Rate: 43 Pesos to Dollars
- Current MXN Exchange Rate: 555 Pesos to Dollars
- Current MXN Exchange Rate: 429 Pesos to Dollars