The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which was meticulously established on April 1, 1935, stands as the cornerstone of India’s financial architecture, serving as the nation’s central bank. Born out of the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission, the RBI was founded with the overarching aim of stabilizing the Indian currency, fostering economic growth, and ensuring the orderly functioning of the country’s financial markets. Its establishment marked a significant milestone in India’s economic history, as it provided a dedicated institution to manage the nation’s monetary and financial affairs.
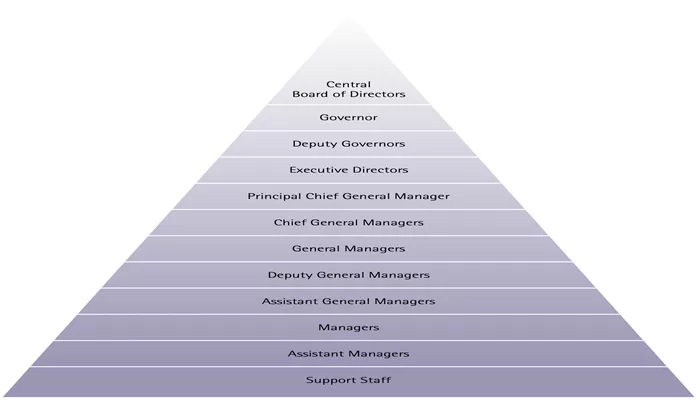
Top Management Positions
Governor
The Governor of the RBI is the highest – ranking official. This individual is responsible for overall leadership and strategic direction. They play a crucial role in formulating and implementing monetary policies. For example, during periods of high inflation, the Governor decides on interest rate hikes to control the money supply. The current Governor of the RBI is Shaktikanta Das. The Governor is appointed by the central government and usually has a term of office. They need to have in – depth knowledge of economics, finance, and monetary theory, as well as excellent leadership and decision – making skills.
Deputy Governors
There are typically up to four Deputy Governors in the RBI. Each Deputy Governor is assigned specific areas of responsibility. Some may focus on monetary policy, others on bank regulation and supervision, or foreign exchange management. For instance, a Deputy Governor in charge of bank regulation will be involved in setting and enforcing prudential norms for banks. They work closely with the Governor and other top – level management to ensure the effective functioning of the RBI. Deputy Governors are also appointed by the central government and are expected to have extensive experience in banking, finance, or related fields.
Central Board Members
Official Directors
In addition to the Governor and Deputy Governors, the central board includes other official directors. These are appointed by the central government and contribute to the overall decision – making process at the RBI. They bring different perspectives from various aspects of the financial and economic sectors, helping to make well – informed decisions on matters such as policy formulation, regulatory changes, and financial stability.
Non – official Directors
There are 10 non – official directors appointed by the government from different industries. They represent the interests of various sectors of the economy, such as agriculture, industry, and services. Their input is valuable as they can provide insights into how RBI policies may impact different segments of the society. Additionally, there is 1 government – appointed official and 4 directors elected by the four regional boards. These non – official directors play an important role in ensuring that the RBI’s decisions are in line with the broader economic and social goals of the country.
Departments and Their Positions
Monetary Policy Department
Economists: Economists in the Monetary Policy Department are responsible for analyzing economic data. They study factors such as inflation rates, GDP growth, and employment figures. Based on their analysis, they provide recommendations to the top management regarding monetary policy. For example, if they observe a slowdown in economic growth, they may suggest measures like reducing interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment. These economists need to have a strong academic background in economics, with expertise in macroeconomic analysis and forecasting.
Policy Analysts: Policy analysts in this department are involved in drafting and evaluating monetary policy measures. They assess the potential impact of different policy options on the economy. For instance, when considering a change in the repo rate (the rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks), they will analyze how it may affect inflation, exchange rates, and the overall financial system. Policy analysts should have a good understanding of financial markets, economic policies, and regulatory frameworks.
Banking Regulation and Supervision Department
Bank Inspectors: Bank inspectors are responsible for conducting regular inspections of commercial banks and other financial institutions. They check whether these institutions are complying with RBI regulations, such as capital adequacy norms, anti – money laundering measures, and lending practices. If they find any irregularities, they can take corrective actions. For example, if a bank is found to have insufficient capital, the bank inspector may require the bank to raise additional capital. Bank inspectors need to have a detailed knowledge of banking operations, regulations, and risk management.
Compliance Officers: Compliance officers in this department work closely with banks to ensure that they are following all the rules and regulations set by the RBI. They provide guidance to banks on regulatory compliance and help them develop internal control mechanisms. They also monitor banks’ compliance over time and report any non – compliance issues. Compliance officers should have a strong legal and regulatory background, as well as good communication and relationship – building skills.
Foreign Exchange Management Department
Foreign Exchange Traders: Foreign exchange traders in the RBI are responsible for managing the country’s foreign exchange reserves. They conduct foreign exchange transactions in the international market to maintain the stability of the Indian rupee‘s exchange rate. For example, if the rupee is depreciating rapidly, they may sell foreign currency reserves to increase the supply of foreign currency in the market and support the rupee. These traders need to have in – depth knowledge of international financial markets, exchange rate dynamics, and risk management.
Exchange Rate Analysts: Exchange rate analysts study factors that affect the exchange rate of the Indian rupee, such as international trade balances, capital flows, and global economic trends. Based on their analysis, they provide forecasts and recommendations to the RBI’s management regarding foreign exchange policy. For example, if they anticipate a significant increase in capital outflows, they may suggest measures to strengthen the rupee’s position. Exchange rate analysts should have expertise in international economics and financial market analysis.
Currency Management Department
Currency Issuance Officers: Currency issuance officers are responsible for the production and distribution of currency notes and coins in the country. They work closely with the government – owned mints and presses to ensure an adequate supply of currency. They also monitor the quality of currency in circulation and plan for the replacement of old and damaged notes. For example, when new currency denominations are introduced, currency issuance officers are involved in the logistics of getting the new notes into circulation. They need to have good organizational and logistical skills, as well as an understanding of security features in currency.
Cash Management Specialists: Cash management specialists in this department manage the cash reserves of the RBI. They ensure that there is enough cash available to meet the demands of the banking system and the public. They also work on optimizing the cash holding levels to minimize costs. For example, they may analyze the seasonal patterns of cash demand and adjust the cash reserves accordingly. Cash management specialists should have skills in financial analysis and operations management.
Research and Statistics Department
Researchers: Researchers in the Research and Statistics Department conduct in – depth studies on various economic and financial topics relevant to the RBI’s functions. They may research areas such as the impact of new financial technologies on the banking sector, or the effectiveness of government fiscal policies on the economy. Their research findings provide valuable input for the RBI’s policy – making process. Researchers need to have strong research skills, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and should be able to present their findings clearly.
Statisticians: Statisticians in this department are responsible for collecting, analyzing, and presenting economic and financial data. They develop statistical models to forecast economic trends. For example, they may create models to predict inflation rates or GDP growth. The data and forecasts provided by statisticians are used by other departments within the RBI for policy – making and decision – making. Statisticians should have expertise in statistical methods, data analysis software, and economic data interpretation.
Regional Board Positions
The RBI has four regional boards located in Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, and New Delhi. Each regional board has five members appointed by the central government for a term of four years.
Regional Board Members
Regional board members play an important role in representing the interests of their respective regions. They provide inputs on regional economic and financial issues to the central board. For example, they may inform the central board about the specific credit needs of rural areas in their region or the impact of RBI policies on local small – and medium – sized enterprises. They also help in the implementation of RBI policies at the regional level and act as a link between the RBI and the local financial institutions and businesses.
Conclusion
So, what Positions Are There at the Reserve Bank of India? The Reserve Bank of India has a diverse range of positions, each playing a crucial role in fulfilling its mandate. From the top – level management positions like the Governor and Deputy Governors, who are responsible for overall strategic direction and policy – making, to the various department – level positions such as economists, bank inspectors, and foreign exchange traders, who carry out the day – to – day functions related to monetary policy, bank regulation, and foreign exchange management. The regional board members also contribute significantly by representing regional interests. All these positions, with their unique responsibilities and requirements, work together to ensure the stability and growth of the Indian financial system and economy.
Related topics
- How Often Does New Zealand’s Central Bank Meet?
- Is the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Independent?
- Can I Exchange Money at Bank of China?